The trend toward the use of stock options is gaining more and more supporters every year.
Options are an important component that can bring significant results. However, a large part of the audience is still unaware of all the benefits that can be gained from using options. This is what we will discuss in this article, as well as the very concept of a stock option, its exercise, and the consequences of its use.
Understanding Stock Options
To get acquainted with the topic of stock options, it is worth starting with the definition of the concept. Thus, options are contracts that give the holder the right to buy or sell a certain amount of a company’s assets. In this case, the price remains fixed by the option.
Options can be used as part of an equity compensation system for employees. In this case, it is up to each employee to decide whether they wish to exercise the option. However, the conditions for obtaining option contracts or exercising them may also vary from organization to organization. But some companies offer them as a reward for dedicated work and as additional employee incentives.
There are two main types of options:
- Call options – an option where the buyer receives the right to purchase assets or securities from the seller in the future at a specified price.
- Put options – a type of investment that gives the holder the option to sell existing securities or shares at a predetermined price within a certain period.
It is important to distinguish between the concepts of an option and a share. Whereas a share purchase gives the holder the securities in perpetuity, options are temporary buy-and-sell contracts that will be valid for a set period.
Benefits of Stock Options
Due to their specific structure and content, stock options can bring many benefits to both the employee and the company. The following is worth mentioning here:
- Additional remuneration. Options allow you to additionally reward employees for their inspired and dedicated work. This demonstrates the employee’s value to the company and encourages them to continue to work to their full potential.
- Employee retention. The fact is that options are only the right to buy or sell shares, and such agreements are concluded for a clearly defined period (for example, 4 or 5 years). This means that the employee will remain in his or her current position for the entire period and will not think about leaving. For business owners, this clause is a kind of “insurance” against losing valuable personnel from their team.
- Hedging or risk management. In this way, owners can fix the prices of purchased assets and reduce the risk of possible losses. In addition, the competent use of hedging will reduce possible losses.
It is also worth noting the factor of limited risks, as there are numerous strategies for trading stock options. Proper use of the strategy will minimize losses and work only for successful investment opportunities. However, before you start using strategies for options, you should carefully study its theoretical characteristics.
Periodic distribution of options will also bring additional benefits to the business itself. It will help attract new talent to the organization. Especially if the company makes this aspect visible to the public.
How to Grant and Exercise Stock Options
Grants of option contracts are provided for a specified fee, but such a contract can be part of a compensation package as employee equity compensation. The contract will specify the price for trading (strike price) and the period for exchange. In particular, Forbes notes that the most common vesting period are 30, 60, or 90 days.
Options work as follows: an employee receives securities, and with them, the opportunity to own shares at a lower price compared to buying them on the open market. The further the option expires, the higher the exercise price may become. After all, there is a very low probability that the price of a share can change dramatically in a short period.
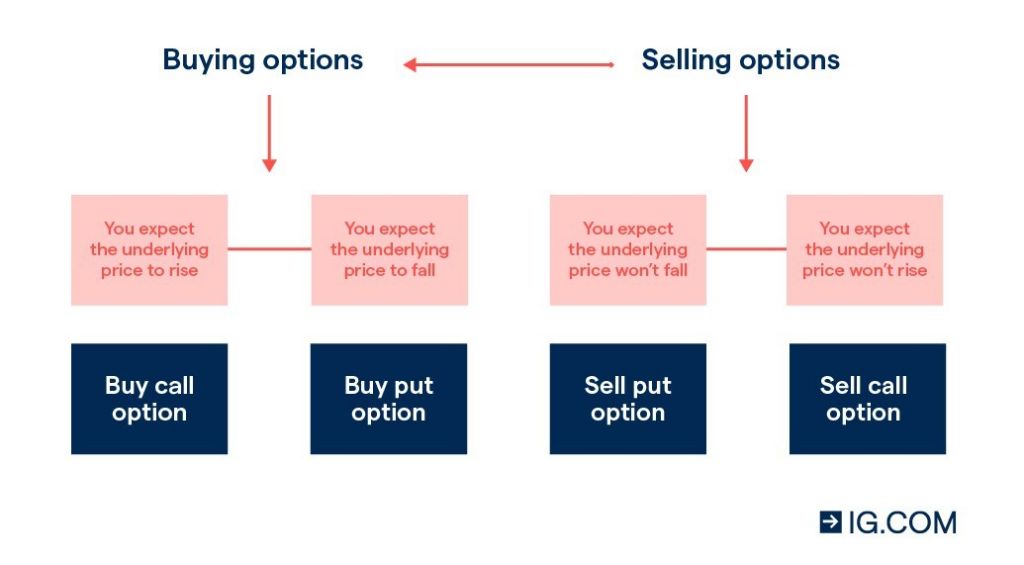
More specifically, the methods of option operation can be seen in a graph prepared by the financial company IG. It clearly shows how, depending on the expectations, the option of further actions, namely buying or selling a put or call option, will differ.
Tax Implications of Stock Options
According to The Internal Revenue Service (IRS), options can be divided into statutory and non-statutory. And at the moment when the owner wants to use ISOs (or incentive stock options), the alternative minimum tax comes into play. It was created to adjust the difference between the market value of the share and the amount paid.
Typically, options are subject to tax in two cases:
- At the time of purchase;
- At the time of sale.
Stock option taxation will directly depend on the type of stock options the participant wishes to use (statutory or non-statutory). For example, when ISO options are exercised, they may be subject to the alternative minimum tax (AMT). This is a special tax system that adjusts the difference between the fair market value of the shares and the amount paid for the shares.
While NSO options will be subject to ordinary income tax. Precisely because ISO options allow the holder to pay taxes only occasionally when exercised, this type is considered more profitable. At the same time, your capital gains can also affect the amount of taxation.
Although the topic of stock options is rather complicated, a careful study of the theoretical material and several practical cases as examples will help to better understand the topic of options, their acquisition, and their use. After all, in the future, this incentive format may receive even more attention and demand.
